Describe in detail the Surgical Procedure Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation.
Describe in detail the Surgical Procedure Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation.
The surgical procedure for hypoglossal nerve stimulation (HNS) to treat obstructive sleep apnea involves implanting a device that electrically stimulates the hypoglossal nerve, which controls tongue movement. The goal is to prevent airway obstruction during sleep. Here's a detailed description of the procedure:
1. **Pre-Surgical Assessment**: Before the surgery, patients undergo a thorough evaluation, including sleep studies and possibly a drug-induced sleep endoscopy to assess airway collapse.
2. **Anesthesia**: The procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
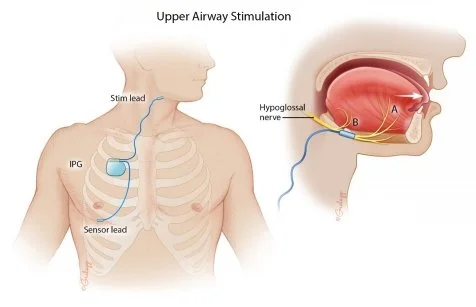
3. **Incision for Device Implantation**: The surgeon makes a small incision, typically under the jaw on the right side of the neck, to access the hypoglossal nerve.
4. **Nerve Identification**: The hypoglossal nerve is carefully identified to ensure proper placement of the stimulation electrode. This step is critical to ensure effective stimulation while minimizing potential damage to the nerve.
5. **Electrode Placement**: Once the nerve is identified, the surgeon places a cuff electrode around it. This electrode is connected to a pulse generator.
6. **Pulse Generator Implantation**: A second incision is made, usually in the upper chest area, to implant the pulse generator. This device is similar in size and appearance to a cardiac pacemaker.
7. **Sensing Lead Placement**: A third incision is often made near the ribcage to place a sensing lead that detects breathing patterns. This lead is connected to the pulse generator.
8. **Device Connection and Testing**: The electrode, sensing lead, and pulse generator are connected. The system may be tested during surgery to confirm proper function.
9. **Incision Closure**: All incisions are closed with sutures or surgical staples.
10. **Recovery**: After surgery, patients typically spend a short time in the hospital for monitoring. Full recovery may take a few weeks, during which patients may experience some pain and swelling.
11. **Device Activation and Calibration**: The device is usually activated a few weeks after surgery to allow for healing. The settings are adjusted to optimize the balance between effectiveness in preventing airway collapse and comfort during sleep.
12. **Follow-Up**: Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor the patient's response to therapy and adjust device settings as needed.
It's important to note that HNS is a specialized procedure and should be performed by a surgeon experienced in this technique. Patients should discuss the risks and benefits with their healthcare provider to understand the potential outcomes and postoperative care requirements.